Centralized Control
Centralized Control in Building Management Systems (BMS)
Centralized Control in Building Management Systems (BMS) refers to a unified approach for managing and controlling various building systems and operations from a single, centralized platform. This integration enables efficient monitoring, automation, and optimization of systems such as HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management, leading to enhanced operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved building performance.
Understanding the a Centralized Control in Building Management Systems (BMS)
Centralized Control in BMS involves the integration of multiple building systems and their management through a single, central control platform. Key components include:
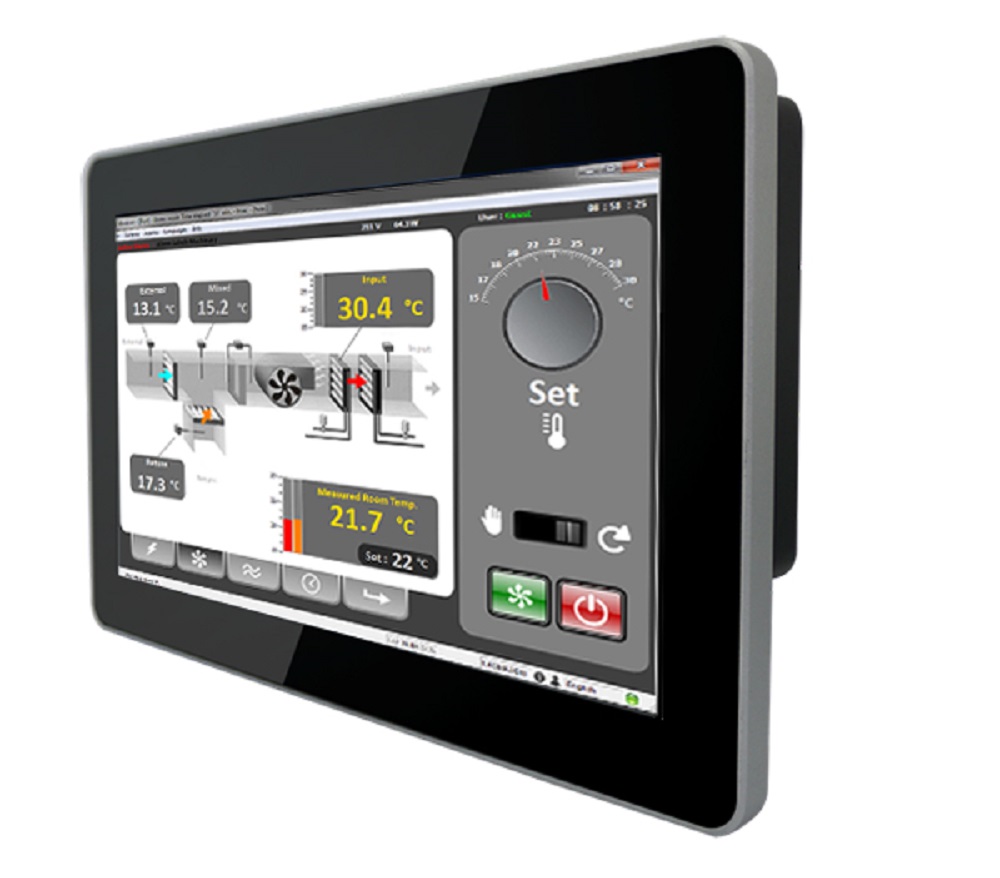
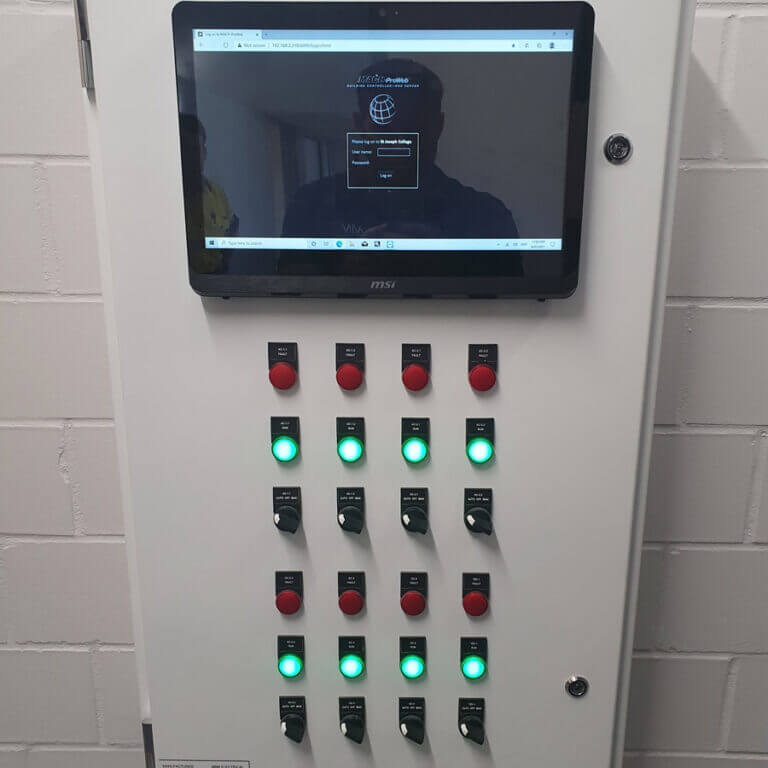
- Central Control Platform: A unified software or hardware interface that consolidates control and monitoring of various building systems, including HVAC, lighting, security, and energy management.
- Integration: The process of connecting different systems and devices, such as sensors, controllers, and actuators, to the central control platform to enable comprehensive management and automation.
- Automation: The use of programmed schedules, triggers, and algorithms to automate building operations, such as adjusting temperature settings, controlling lighting, or managing energy usage.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Real-time monitoring of building systems, along with data collection and reporting, to provide insights into performance, energy consumption, and system status.
Why Choose a Centralized Control in Building Management Systems (BMS)?
- Improved Efficiency: Centralized control allows for the efficient management of multiple systems from a single interface, reducing the complexity of operations and improving overall building performance.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing system operations and energy use, centralized control helps reduce operational costs and energy consumption, leading to significant cost savings over time.
- Enhanced Automation: Automation capabilities allow for the scheduling and coordination of building systems, improving comfort and reducing the need for manual adjustments.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Centralized control provides real-time monitoring and alerts for system performance and faults, enabling prompt response and minimizing downtime.
- Data-Driven Insights: Access to comprehensive data and analytics allows for better decision-making, performance optimization, and identification of areas for improvement.
- Integration with Other Systems: Centralized control can be integrated with other building systems, such as fire alarms and security systems, providing a cohesive approach to building management and safety.