Energy Management
Energy Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)
Energy Management in Building Management Systems (BMS) involves the integration and optimization of energy consumption and efficiency within a building through centralized monitoring and control. By leveraging advanced technologies and data analytics, BMS can help reduce energy costs, enhance sustainability, and improve overall building performance.
Understanding the a Energy Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)
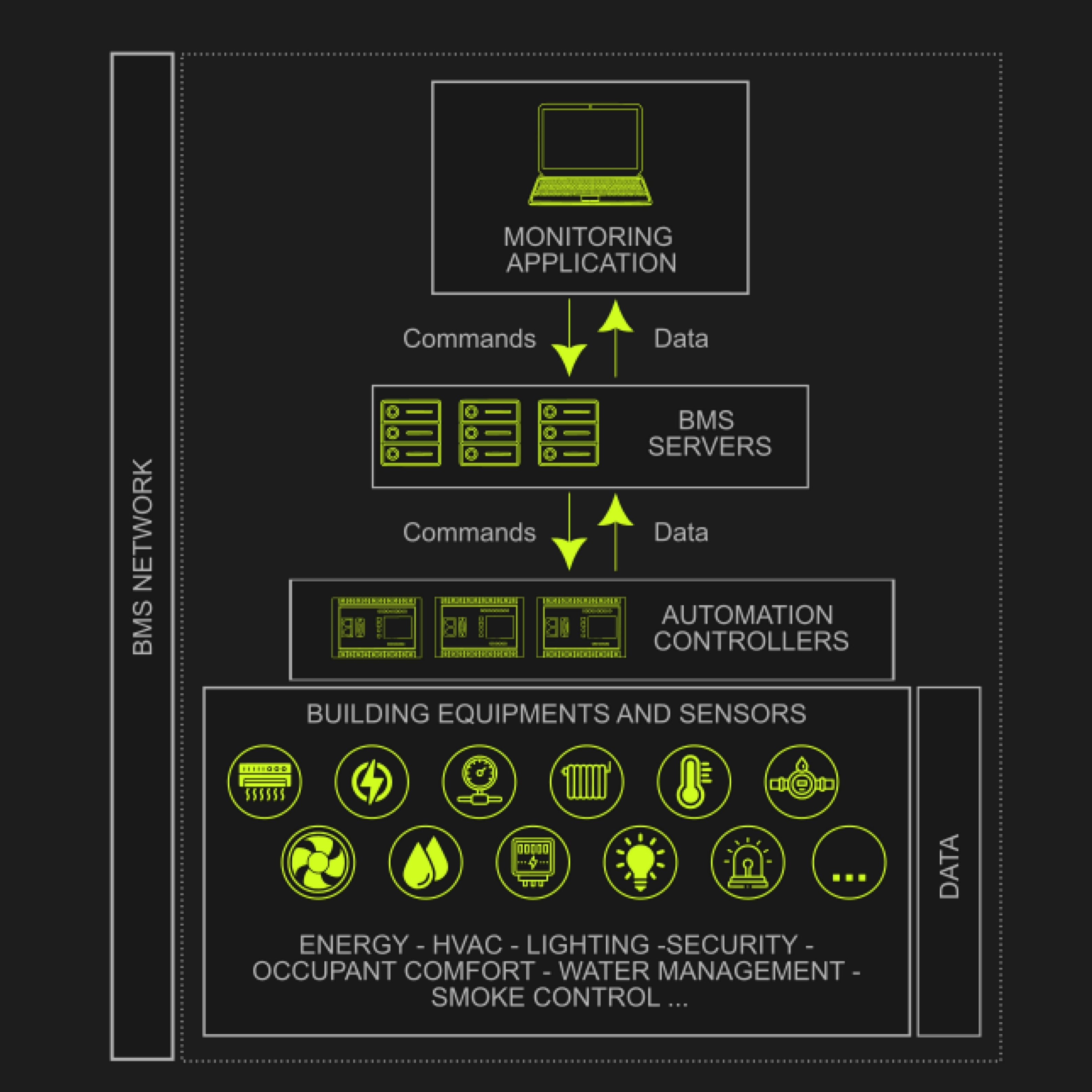
Energy Management in BMS refers to the systematic monitoring and control of energy usage across various building systems and processes. Key components and features include:
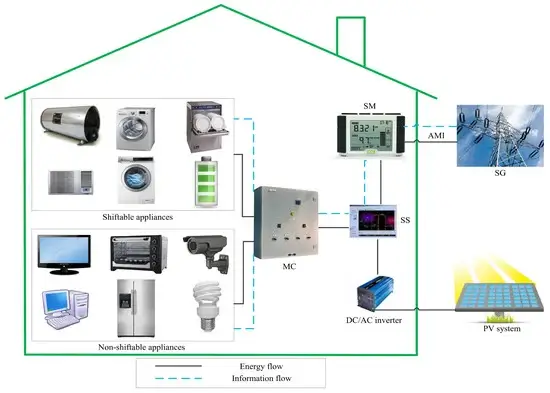
- Centralized Energy Management Platform: A unified interface within the BMS that consolidates data on energy consumption, performance metrics, and system status from various building systems.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of energy usage across HVAC, lighting, and other systems to identify patterns, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing energy consumption data to identify trends, predict usage, and make informed decisions about energy efficiency measures and upgrades.
- Automated Control: Implementing automation strategies to optimize energy use, such as adjusting HVAC settings based on occupancy, using timers for lighting, and managing peak load demand.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Sources: Incorporating solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources into the energy management strategy to enhance sustainability and reduce reliance on conventional energy.
Why Choose a Energy Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)?
- Cost Savings: Effective energy management strategies can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills, resulting in substantial cost savings for building operators and occupants.
- Enhanced Sustainability: By optimizing energy usage and incorporating renewable energy sources, BMS contributes to a building’s sustainability goals and reduces its carbon footprint.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Centralized energy management allows for better coordination and optimization of building systems, enhancing overall operational efficiency and comfort.
- Real-Time Insights and Reporting: Access to real-time data and analytics enables informed decision-making, supporting continuous improvement and the identification of energy-saving opportunities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Implementing effective energy management practices helps ensure compliance with local energy efficiency regulations and standards, mitigating potential legal risks.
- Increased Building Value: Energy-efficient buildings are often more attractive to tenants and buyers, potentially increasing property value and marketability.