HVAC Management
HVAC Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)
HVAC Management in Building Management Systems (BMS) involves the integration and control of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems from a centralized platform. This approach enhances the efficiency, comfort, and performance of HVAC systems by providing real-time monitoring, automated control, and data-driven insights. Effective HVAC management within a BMS ensures optimal indoor climate, energy savings, and improved operational efficiency.
Understanding the a HVAC Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)
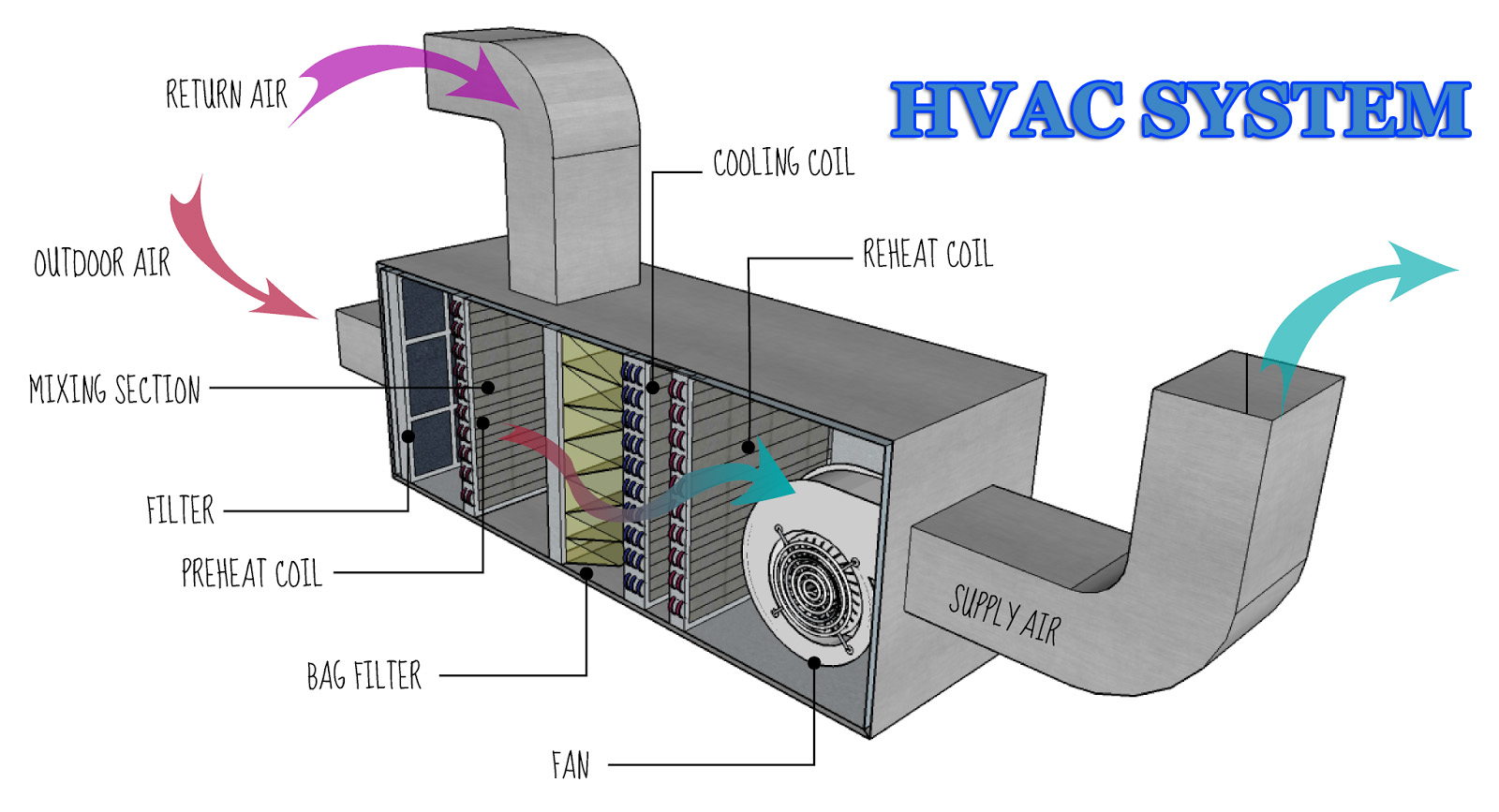
HVAC Management in BMS refers to the centralized control and monitoring of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems through a Building Management System. Key components and functions include:
- Centralized Control Platform: A unified interface that allows for the control and management of HVAC systems, including temperature settings, fan speeds, and operational modes.
- Integration with Building Systems: The connection of HVAC systems with other building systems, such as lighting and occupancy sensors, to optimize performance and energy use.
- Automation and Scheduling: The ability to program schedules and triggers for HVAC operations based on factors such as time of day, occupancy levels, and outdoor weather conditions.
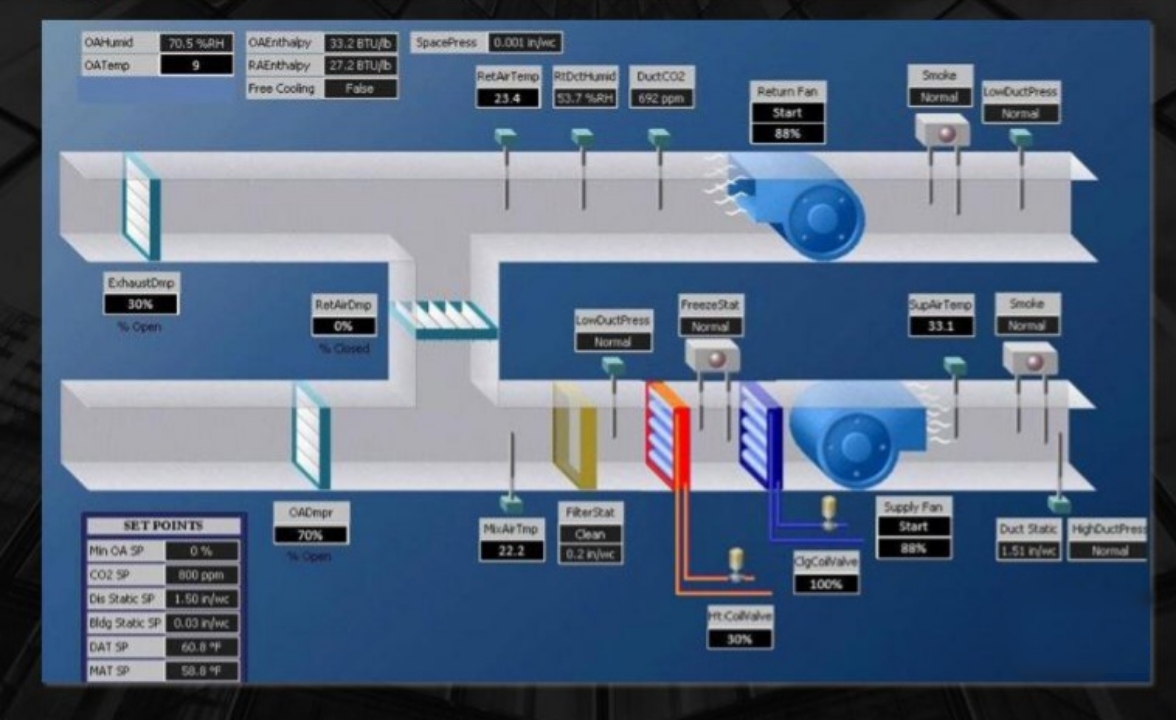
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of HVAC system performance, including temperature, humidity, and air quality, to ensure optimal operation and identify potential issues.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering and analyzing data on HVAC system performance, energy consumption, and environmental conditions to inform decision-making and improvements.
Why Choose a HVAC Management in Building Management Systems (BMS)?
- Enhanced Comfort: Centralized HVAC management ensures consistent and comfortable indoor climate conditions by adjusting temperature and ventilation based on real-time data and user preferences.
- Energy Efficiency: Automation and optimization features help reduce energy consumption by adjusting HVAC operations based on occupancy and environmental conditions, leading to lower energy costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Centralized control simplifies the management of HVAC systems, streamlining operations, reducing manual intervention, and improving overall system performance.
- Real-Time Alerts and Diagnostics: Immediate notification of system faults or performance issues allows for prompt maintenance and repair, minimizing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns.
- Data-Driven Insights: Access to detailed data and analytics provides valuable insights into HVAC system performance, energy use, and potential areas for optimization, supporting informed decision-making.
- Integration with Other Systems: Seamless integration with lighting, security, and other building systems allows for coordinated operation and enhanced overall building management.