Occupant Comfort
Occupant Comfort in Building Management Systems (BMS)
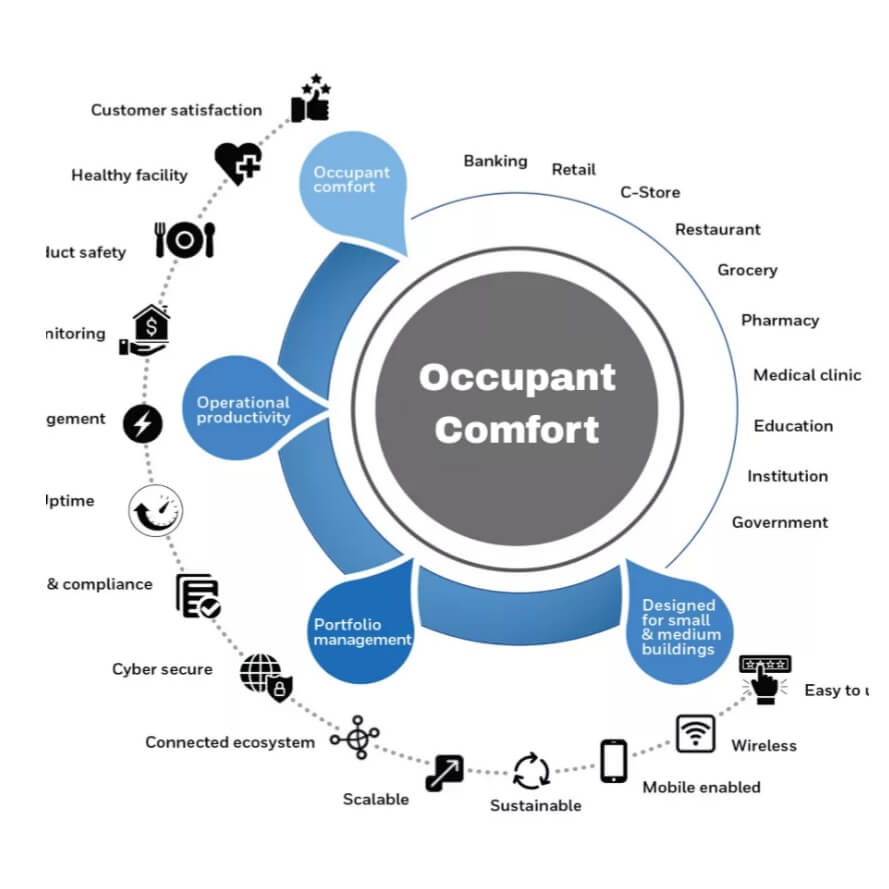
Occupant Comfort in Building Management Systems (BMS) focuses on optimizing the indoor environment to enhance the well-being and satisfaction of building occupants. By integrating various building systems—such as HVAC, lighting, and environmental controls—into a BMS, facilities can ensure that temperature, air quality, lighting, and other factors are adjusted to create a comfortable and productive atmosphere.
Understanding the a Occupant Comfort in Building Management Systems (BMS)
Occupant Comfort in BMS involves the management and optimization of building systems to ensure a pleasant and healthy indoor environment. Key components and features include:
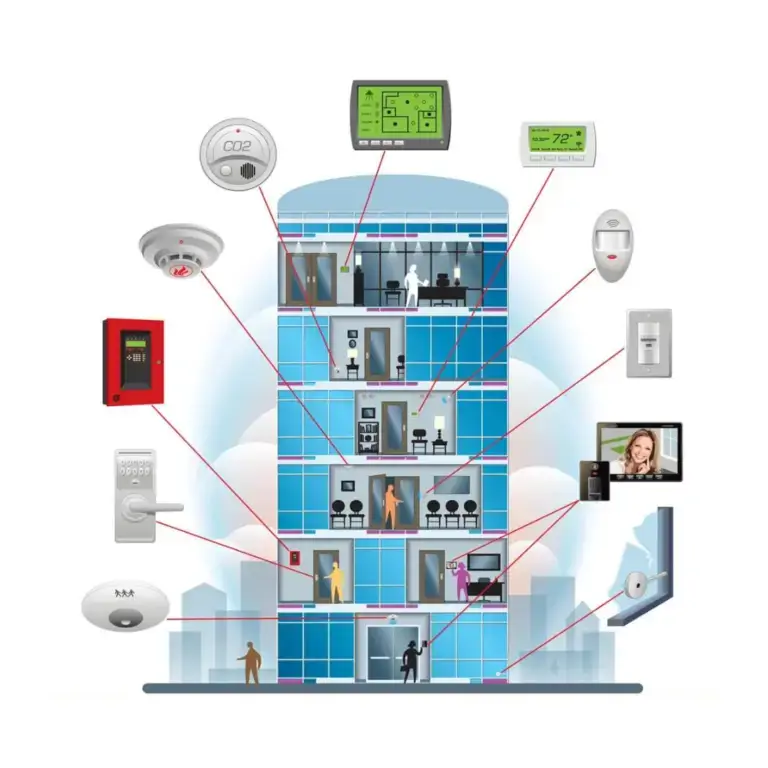
- Centralized Control Platform: A unified interface within the BMS that allows for the management of various systems affecting occupant comfort, including HVAC, lighting, and environmental controls.
- Temperature Control: Monitoring and adjusting HVAC systems to maintain optimal temperature levels throughout the building, considering both seasonal changes and individual preferences.
- Air Quality Management: Managing ventilation and filtration systems to ensure good indoor air quality by controlling factors such as humidity, CO2 levels, and particulate matter.
- Lighting Control: Adjusting lighting systems based on occupancy, time of day, and natural light availability to enhance visibility and reduce eye strain while creating a pleasant ambiance.
- Personalized Settings: Providing options for occupants to customize their individual environment, such as adjusting temperature or lighting levels, to meet personal preferences and needs.
Why Choose a Occupant Comfort in Building Management Systems (BMS)?
- Enhanced Well-Being: Optimizing environmental conditions such as temperature, air quality, and lighting directly contributes to the comfort and health of building occupants, improving overall satisfaction.
- Increased Productivity: A comfortable environment helps reduce discomfort and distractions, leading to increased productivity and performance, especially in office and workspaces.
- Energy Efficiency: Effective management of heating, cooling, and lighting systems can reduce energy consumption by ensuring that systems operate only when needed and at optimal levels.
- Customizable Comfort: Allowing occupants to adjust their individual settings provides a personalized experience, ensuring that each person’s preferences are met without compromising overall efficiency.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustments: Continuous monitoring and real-time adjustments of environmental conditions help maintain a stable and pleasant indoor climate, addressing issues before they affect occupant comfort.
- Data-Driven Insights: Analyzing data on environmental conditions and occupant feedback helps identify areas for improvement and informs strategies to enhance overall comfort and satisfaction.