Network Infrastructure
Network Infrastructure
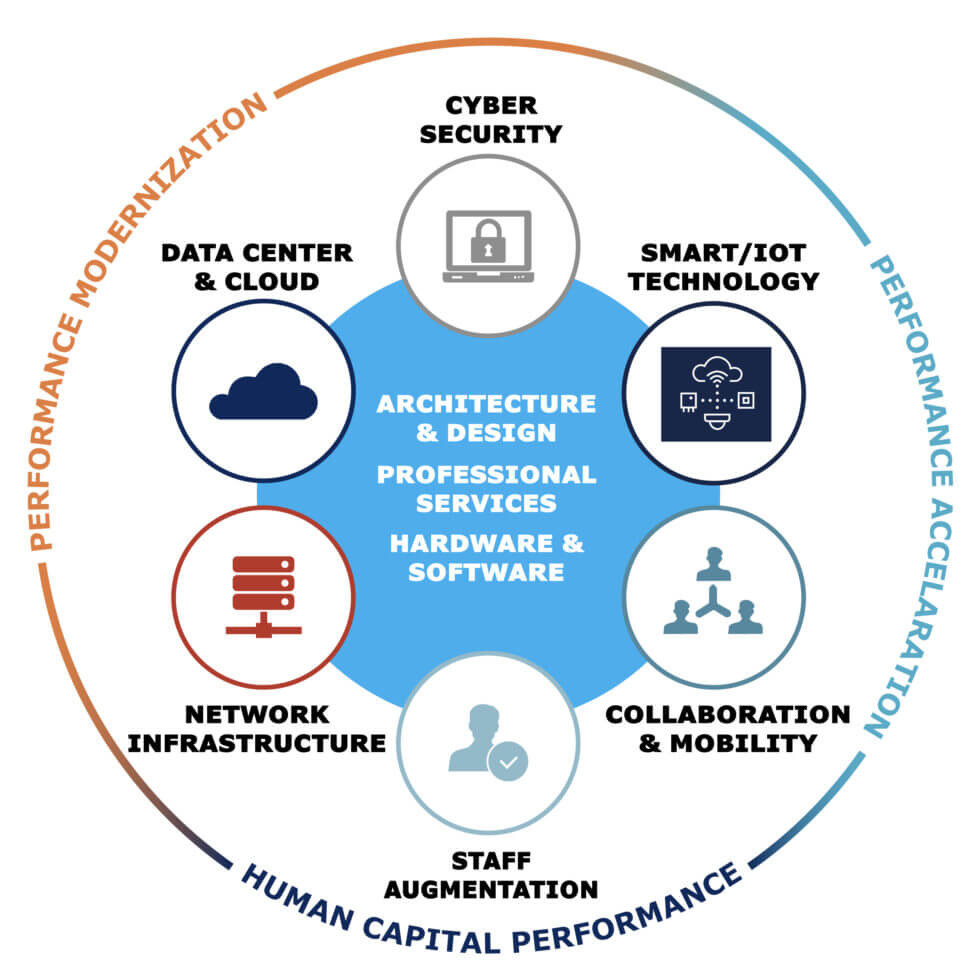
Design, implementation, and management of secure and scalable network solutions with secure and high-performance wireless networks, Fine-tuning network configurations, and Proactive monitoring, maintenance, and management for enhanced mobility and connectivity between users, devices, apps, the internet, and more. Network infrastructure is the combination of multiple hardware and software.
By hardware, I am referring to the physical network switches and routers. Software resources can be virtualized switches, routers, firewalls, and load balancers. Thus, we can categorize the infrastructure into wired, wireless, and hybrid.
We build a Local Area Network (LAN) which is a private, high-speed network that connects computers and other devices in a limited geographical area like a school, office, or home. With it, we can provide networking facilities to a larger collective of users and equipment. It enables efficient communication and resource sharing among connected devices to facilitate collaboration, data exchange, and centralized network management. However, LAN has a range of around 1-10 kilometers in radius.
Understanding the a Network Infrastructure
Network Infrastructure refers to the physical and logical components that make up a network, enabling the connectivity, communication, and management of data between devices and systems. It includes:
- Hardware: Routers, switches, servers, firewalls, and network cables that facilitate data transmission and connectivity.
- Software: Network management software, operating systems, and security applications that oversee network performance, configuration, and security.
- Protocols: Rules and standards such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and DNS that govern data exchange and communication between devices.
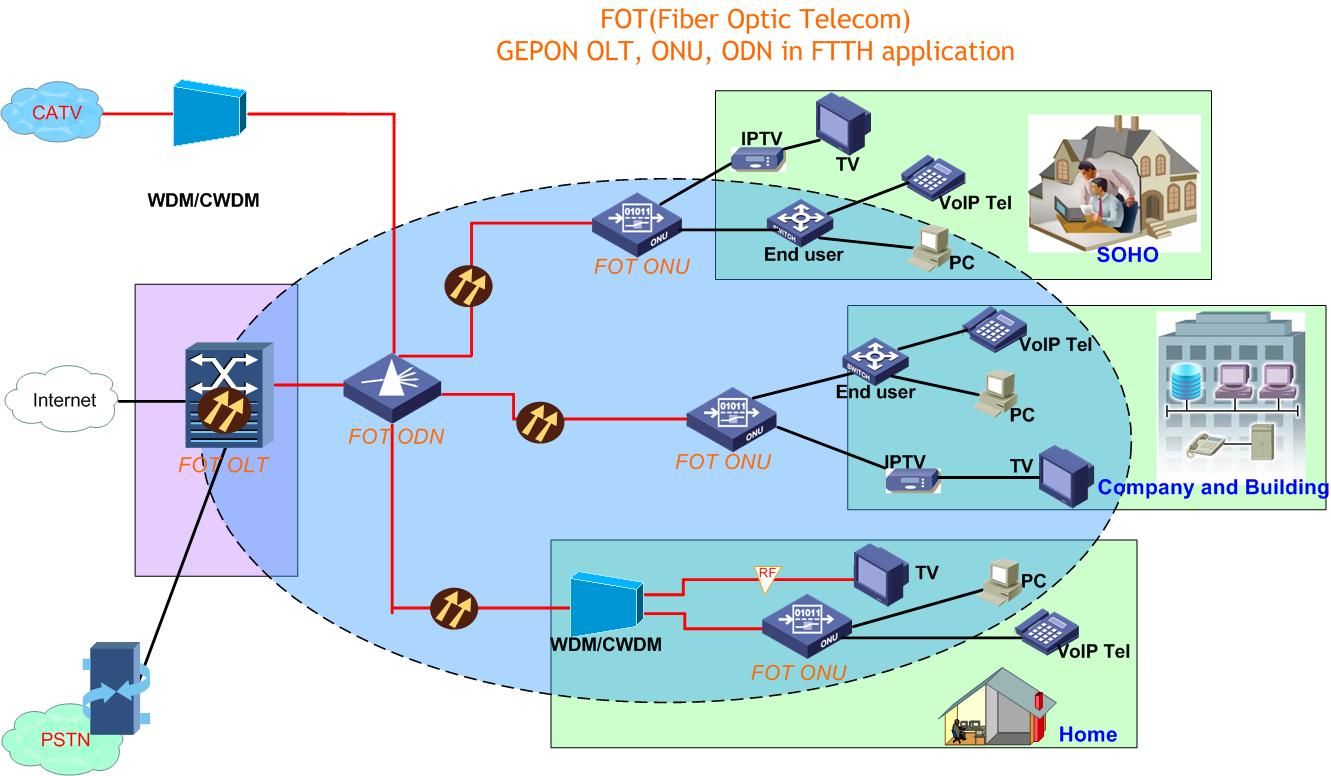
- Connectivity: Various methods of connecting devices, including wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) technologies. Network infrastructure supports a range of activities from data exchange and internet access to internal communication and remote access.
Why Choose a Network Infrastructure?
- Reliable Connectivity: A well-designed network infrastructure ensures consistent and reliable connectivity, minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
- Scalability: Network infrastructure can be designed to accommodate growth, allowing for the easy addition of new devices, users, and services as business needs evolve.
- Performance Optimization: Effective network design and management optimize performance by balancing loads, minimizing latency, and ensuring efficient data transfer.
- Security: Robust network infrastructure includes security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Flexibility and Integration: Network infrastructure supports integration with various technologies and systems, enabling seamless communication and collaboration across different platforms and locations.
- Cost Efficiency: A well-planned network infrastructure can reduce costs associated with downtime, maintenance, and inefficient data management, providing a cost-effective solution for business operations.